|
Let A1, A2,..........Ak be a collection of mutually exclusive and exhaustive possible events. Then for any other possible event 'B':

The notation P(A|B) means the probability of 'A' given that 'B' has occurred.
A medical procedure has a 90% probability of correctly diagnosing a medical condition. However if the subject does not have the condition there is a 1% probability of making a faulty diagnosis.
If one person in ten thousand suffers from the condition, what is the probability that a person selected at random who returns a positive result actually suffers from the condition.
The probabilities are:
| |
|
Probability
|
| A |
they have the condition |
|
| B |
they return a positive result |
|
| A1 |
they have the condition |
0.0001 |
| A2 |
they do not have the condition |
0.9999 |
| P(B|A1) |
they return a positive result given that they have the condition |
0.90 |
| P(B|A2) |
they return a positive result when they do not have the condition |
0.01 |
| P(A1|B) |
the probability they have the condition, given the positive result |
0.0089 |
This is highly non-intuitive. The answer stands because the condition is extremely rare, and the number of false positives outweighs the number of correct diagnoses.
| Complementary Probability |
|
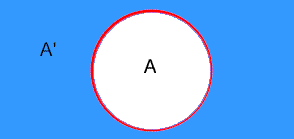
The complement of a set A is the set of all outcomes that are not contained in A, denoted by A':
The outcome of all the events that are in both A and B. Intersection is roughly equivalent to "and":
The multiplication rule states that:
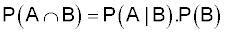
There is a 0.01 (1%) probability that a seal will fail if the joint is not coated with a sealing compound before assembly. The proportion of joints that are not coated is 0.05 (5%).
What is the probability that a seal will fail.
| P(A|B) |
Probability that the seal will fail if not coated |
0.01 |
| P(B) |
Probability the seal will not be coated |
0.05 |
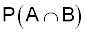 |
0.01 x 0.05 |
=0.0005 |
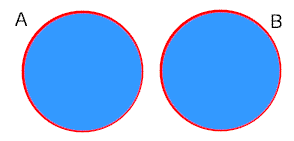
Events that are mutually exclusive, eg. a head and a tail on a coin toss:
The chance of something happening. The probability of getting a head on a coin toss is 0.5.
Probability can also be viewed as the fraction of occurrences over a large number of trials. If the results from many coin tosses are recorded the proportion of heads will be close to 50% (assuming a fair game).
The outcome of all the events that include A or B. Union is roughly equivalent to "or":
A diagram used to illustrate the concepts of probability. Venn diagrams are used in the entries for 'Union', 'Intersection' and 'Complement'.
|